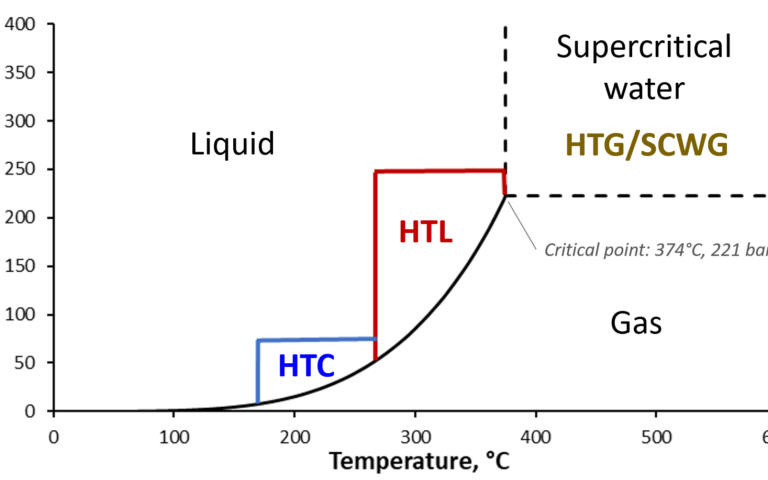
Sludge thermochemical treatment − an overview
Thermochemical methods are used for either:
- significantly reducing the sludge solids content, or
- pre-treating sludge upstream of anaerobic digestion (AD) to increase the biodegradability of the organic carbon.
When operated at elevated temperatures, i.e. for solids destruction/conversion rather than AD pre-treatment, energy is generated from the carbon content. The energy is recoverable either as heat or a combustible material (solid, liquid or gas), depending on the type of process.