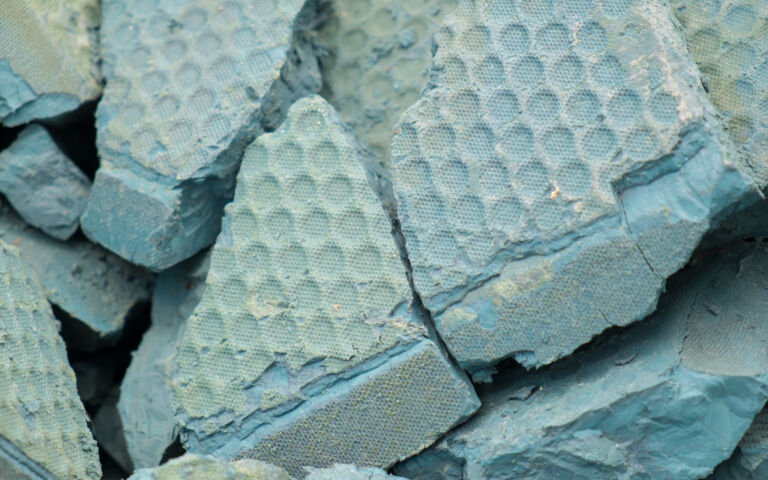
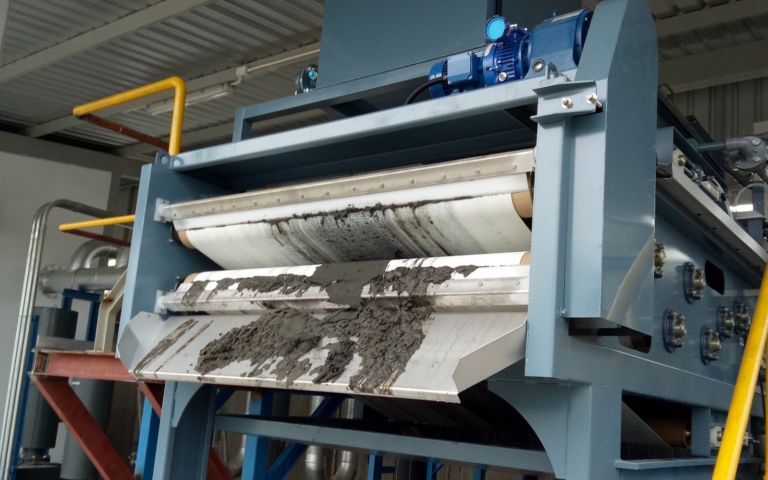
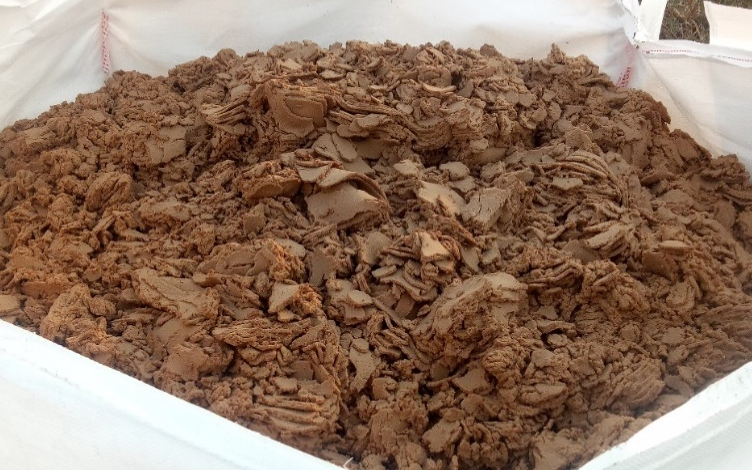
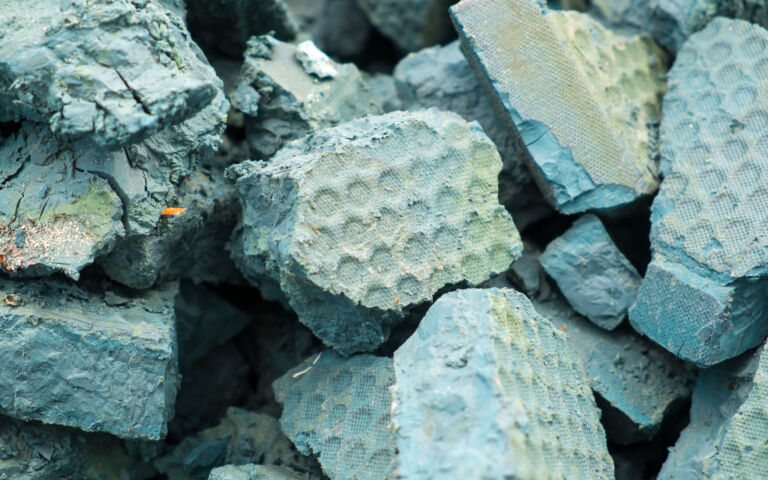
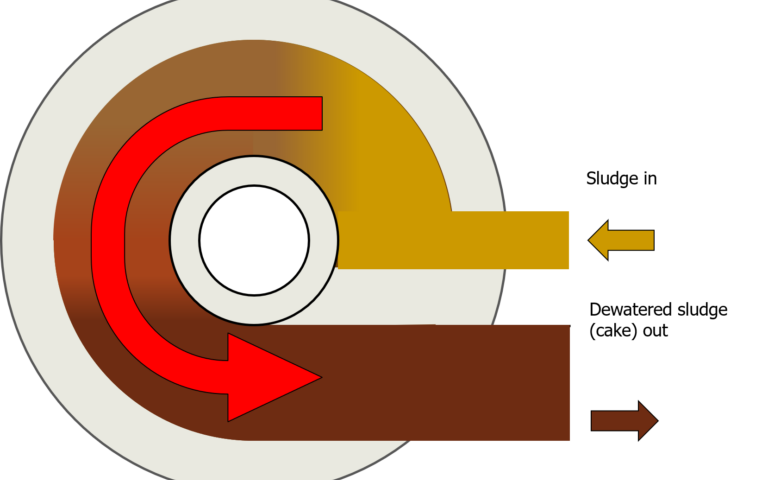
Introduction to sludge dewatering
Dewatering processes provide a concentrated, consolidated product − retaining most of the solids from the original sludge – along with a diluted stream which is predominantly water.
Dewatering processes apply a significant mechanical force to achieve increased water removal over that possible from thickening.