What is sludge?
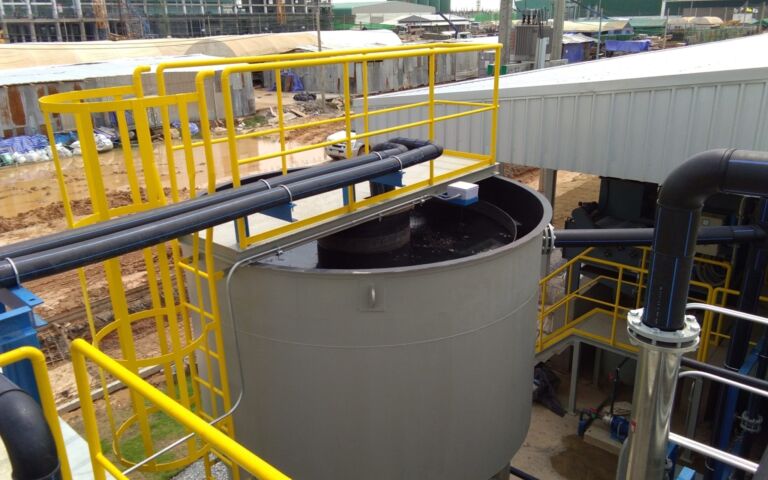
For conventional municipal wastewater treatment, there are two main sludge streams. The first is from the primary sedimentation stage, producing primary sludge. The secondary stream is from the biological treatment stage, producing waste activated sludge (WAS), if the biological treatment is based on the activated sludge process.
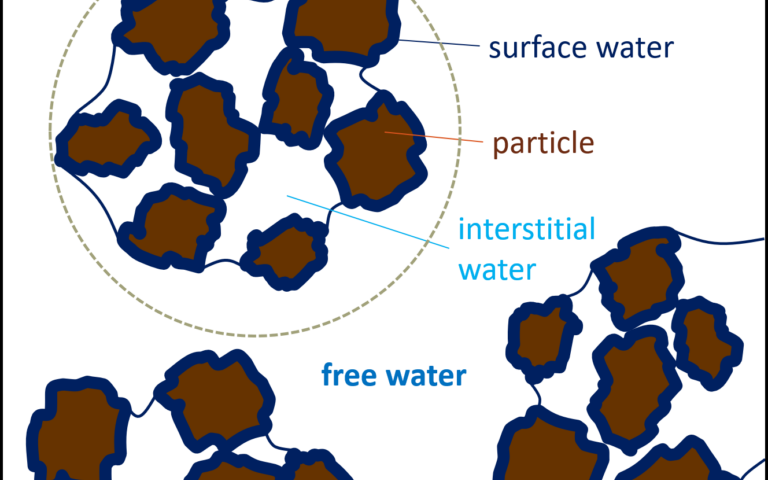
Regardless of its origins, sludge contains water, dissolved organic and inorganic materials and suspended solids. The suspended solids normally make up 2−5% of the sludge for municipal wastewater sludge.